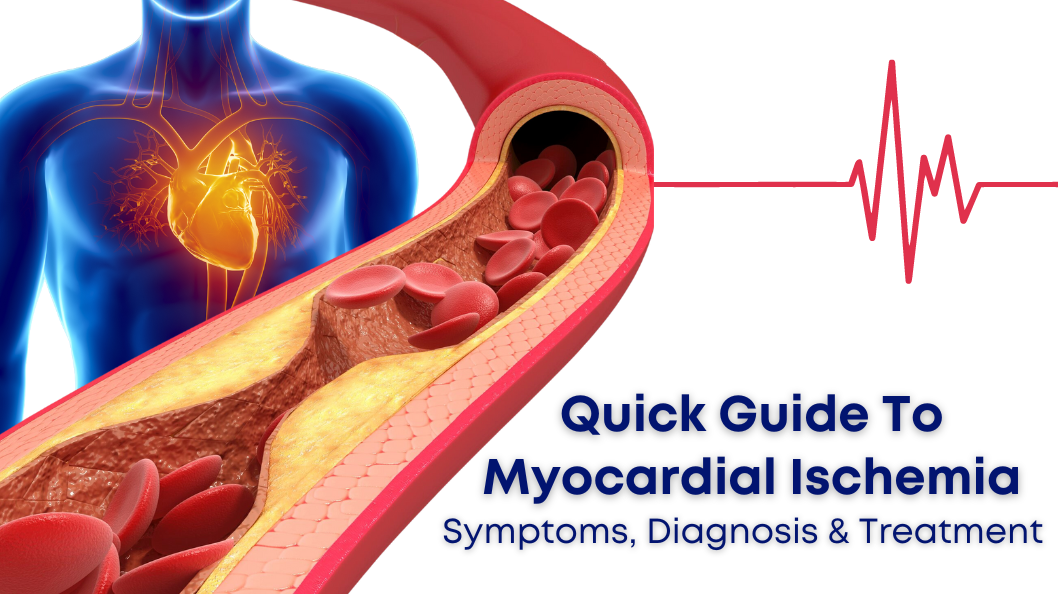
Quick Guide to Myocardial Ischemia: Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment
Myocardial ischemia is a common heart condition characterized by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to inadequate oxygen supply. This ischemic imbalance can result in chest pain, discomfort, and potentially life-threatening complications such as heart attack. Understanding the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for myocardial ischemia is crucial for early intervention and prevention of adverse outcomes. Additionally, advancements in medical technology, such as Clarity Medical's TMT (Treadmill Test) machines, are playing a vital role in accurately diagnosing this condition. In this article, we will explore the nuances of myocardial ischemia, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and the impact of Clarity Medical's TMT machines on diagnostics.
What is Myocardial Ischemia?
Myocardial ischemia occurs when the blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium) is reduced, usually due to narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries. This inadequate blood supply deprives the heart muscle of oxygen and nutrients, leading to ischemic injury and potential damage to the heart tissue.
Symptoms of Myocardial Ischemia:
The symptoms of myocardial ischemia can vary depending on the severity and duration of blood flow restriction. Common symptoms may include:
> Angina: Chest pain or discomfort is the hallmark symptom of myocardial ischemia. It may feel like pressure, tightness, squeezing, or a heavy sensation in the chest. The pain may radiate to the arms, shoulders, neck, jaw, or back.
> Shortness of Breath: Myocardial ischemia can cause breathlessness, especially with exertion or physical activity. Individuals may experience difficulty breathing or a sensation of air hunger.
> Fatigue: Persistent fatigue or weakness may occur, often accompanied by reduced exercise tolerance or stamina.
> Nausea and Dizziness: Some individuals with myocardial ischemia may experience nausea, light-headedness, or dizziness, particularly during episodes of chest pain.
> Sweating: Profuse sweating, clamminess, or diaphoresis may accompany episodes of myocardial ischemia.
What Causes Myocardial Ischemia?
Myocardial ischemia is primarily caused by atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque (fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances) within the coronary arteries. The narrowing or blockage of these arteries reduces blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to ischemic events. Common risk factors for atherosclerosis and myocardial ischemia include:
> Hypertension: High blood pressure can damage the arterial walls and promote the formation of atherosclerotic plaques.
> Hyperlipidaemia: Elevated levels of cholesterol, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis.
> Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that can damage the blood vessels and accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis.
> Diabetes: Diabetes mellitus is associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis and myocardial ischemia due to elevated blood sugar levels and metabolic abnormalities.
> Obesity: Excess body weight and abdominal obesity are risk factors for metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and atherosclerosis.
> Physical Inactivity: Lack of regular exercise and sedentary lifestyle habits can predispose individuals to obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidaemia, increasing the risk of myocardial ischemia.
How is Myocardial Ischemia Diagnosed?
Diagnosing myocardial ischemia typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and cardiac tests. Key diagnostic modalities include:
> Electrocardiogram (ECG): ECG is a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart. Changes in the ECG pattern, such as ST-segment depression, T-wave inversion, or the development of Q waves, may indicate myocardial ischemia or infarction.
> Stress Testing: Stress testing, such as exercise treadmill testing (TMT) or pharmacological stress testing, is performed to evaluate the heart's response to physical exertion or pharmacological stress. Exercise-induced changes in ECG patterns or symptoms suggestive of myocardial ischemia during stress testing may indicate coronary artery disease.
> Echocardiography: Echocardiography uses sound waves to create images of the heart's structure and function. It can assess for regional wall motion abnormalities, reduced left ventricular function, or evidence of ischemia-induced changes in cardiac function.
> Coronary Angiography: Coronary angiography is an invasive procedure that involves injecting contrast dye into the coronary arteries to visualize any blockages or narrowing of the arteries. It is considered the gold standard for diagnosing coronary artery disease and myocardial ischemia.
How Can Myocardial Ischemia Be Treated?
Treatment for myocardial ischemia aims to relieve symptoms, improve blood flow to the heart muscle, and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment options may include:
> Medications: Medications such as antiplatelet agents (aspirin, clopidogrel), statins, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and nitro-glycerine may be prescribed to reduce the workload on the heart, lower cholesterol levels, control blood pressure, and relieve chest pain.
> Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle changes, including adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress, are essential components of myocardial ischemia management.
> Revascularization Procedures: In cases of severe or symptomatic coronary artery disease, revascularization procedures such as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with stent placement or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) may be recommended to restore blood flow to the affected areas of the heart.
> Cardiac Rehabilitation: Cardiac rehabilitation programs offer structured exercise training, education, and support services to individuals recovering from myocardial ischemia or other cardiovascular events. These programs help improve cardiovascular fitness, reduce cardiac risk factors, and enhance overall quality of life.
How Clarity Medical's TMT Machines Are Impacting Diagnoses:
Clarity Medical's TMT (Treadmill Test) machines are instrumental in the accurate diagnosis of myocardial ischemia and other cardiovascular conditions. Key features and benefits of Clarity Medical's TMT machines include:
> Advanced Monitoring: Clarity Medical's TMT machines offer real-time monitoring of ECG parameters, blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation during stress testing, allowing healthcare providers to assess the heart's response to physical exertion accurately.
> Customizable Protocols: The TMT machines feature customizable exercise protocols tailored to individual patient needs and fitness levels, ensuring optimal stress testing conditions and accurate assessment of cardiovascular function.
> User-Friendly Interface: The user-friendly interface of Clarity Medical's TMT machines simplifies the stress testing process for both healthcare providers and patients, ensuring efficient data acquisition and interpretation.
Conclusion:
Myocardial ischemia is a common cardiovascular condition characterized by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle, leading to ischemic injury and potential complications. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are essential for reducing the risk of adverse outcomes and improving patient outcomes. Clarity Medical's TMT machines play a crucial role in accurately diagnosing myocardial ischemia and guiding treatment decisions, helping healthcare providers deliver optimal care to patients with cardiovascular disease. With continued advancements in medical technology and innovative diagnostic tools, the prognosis for individuals with myocardial ischemia continues to improve, offering hope for better outcomes and enhanced quality of life.